Scarring is a common outcome of injuries, surgeries, and certain skin conditions. It occurs as a result of the body's natural healing process, in which collagen fibers are produced to repair damaged tissue. While scars cannot be completely eliminated, there are several measures that can be taken to prevent or reduce their appearance. In this article, we will discuss the causes of scarring, the different types of scars, and the various methods of preventing and treating scars.
Causes of Scarring
Scars can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, surgeries, burns, acne, and certain skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. They are a natural part of the body’s healing process to repair damaged skin and close gaps due to injury. Scarring occurs when the dermis is damaged. The severity of a scar depends on the depth and size of the wound, as well as the person's individual wound healing response. In general, deeper wounds and larger wounds are more likely to result in more noticeable scars.
Types of Scars
There are several different types of scars, each with its own unique characteristics. The most common types of scars include:
- Cicatrix: these are normal, fine-line scars that are usually flat.
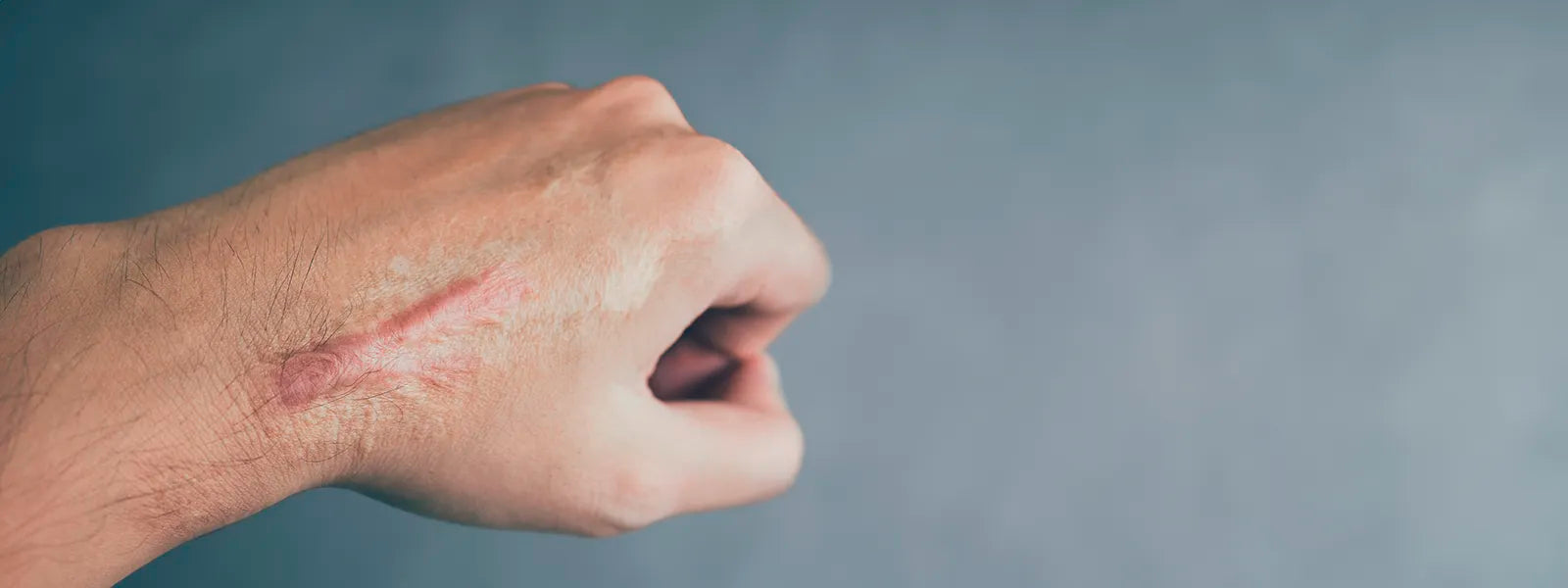
- Keloid scars: These are raised, thick, and bumpy scars that extend beyond the original wound. They are more common in people with darker skin tones and can be itchy and painful.
- Hypertrophic scars: These raised scars are similar to keloid scars, but they do not extend beyond the boundaries of the original wound. They are also raised and thick, but they are generally less itchy and painful.
- Atrophic scars: These are sunken, pitted scars, often known as acne scars, that occur as a result of a loss of tissue. They are most commonly caused by acne, chickenpox, or injuries that result in the destruction of skin cells.
Preventing Scarring
While it is not possible to completely prevent scarring, there are several measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing noticeable scars. Preventing scar formation is essential to reduce the size and appearance of scarring. These include:
- Keep the wound clean: Proper wound care is essential for preventing infection and reducing the risk of scarring. Wounds should be washed gently with mild soap and water and covered with a bandage to protect them from dirt and bacteria.
- Use Petroleum Jelly: Use petroleum jelly to keep the wound moist. Wounds often dry out and form scabs which take longer to heal. Additionally scabs tend to be itchy which if picked at can leave large scars.
- Avoid picking at scabs: Picking at scabs can damage the healing tissue and increase the risk of scarring. It's important to allow scabs to fall off naturally.
- Protect With Bandages: After cleaning, apply an adhesive bandage to protect the wound area. Change the bandage daily to keep the area clean. If a bandage hurts the skin, try gauze pad with paper tape.
- Use sunscreen: Sun exposure can cause scars to darken and become more noticeable. Sun protection will reduce discoloration and help the scar fade faster. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Massage the scar: Gently massaging a scar can help to soften and flatten it. This can be done using a scar-reducing cream or oil, or simply by using your fingers.
- Consider silicone sheets or gels: Silicone gel sheets and gels have been shown to be effective in reducing the appearance of scars. These products can be found at most drugstores and should be applied to the scar according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Consult Doctor (If Necessary). If a wound is severe enough to require stitches, follow your doctor’s advice.
Treatment for Scarring
For those who have already developed scars, there are several treatment options available. In order for scar treatments to be effective they should be deployed as soon as possible. Young scar tissue is more responsive to scar therapy. The most common treatments include:
- Topical treatments: These include creams, gels, and oils that can be applied directly to the scar to reduce redness, itching, and discomfort.
- Injections: Steroid injections can be used to reduce the size and itchiness of keloid and hypertrophic scars.
- Surgery: Surgery can be used to remove keloid and hypertrophic scars.
- Laser treatment: Laser therapy can be used to reduce the appearance of scars by stimulating collagen production and evening out the skin tone.
It's worth mentioning that according to a study conducted by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, the most effective treatment for scarring depends on the type of scar, the location of the scar, and the individual's skin type. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary for optimal results.
One thing to keep in mind is that according to a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, it's important to seek treatment early on. Scarring can be more difficult to treat if left untreated for an extended period of time. In the same study, it was found that people who sought treatment within three months of injury or surgery had better outcomes than those who waited longer.
Despite the fact that scarring is a natural part of the healing process, it can have a significant impact on a person's physical and emotional well-being. If you are concerned about scarring, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider or a dermatologist to discuss your options. They can help you develop a plan to prevent or reduce the appearance of scars.
In conclusion, Scarring is a natural process that happens after a wound, injury or surgery. The severity of scarring can vary depending on the size and depth of the wound, as well as the individual's healing response. There are several preventative measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of scarring, such as keeping the wound clean, avoiding picking at scabs and using sunscreen. There are also several treatment options available for those who have already developed scars, including topical treatments, injections, surgery, and laser therapy. It's important to seek treatment early on for better outcomes and consult a healthcare provider or a dermatologist for personalized advice.
References:
Proper Wound Care: How To Minimize A Scar | AAD



Leave a comment (all fields required)